Data wrangling & visualization II — dplyr
Week 3
Midterm & Final Exam Format
- closed-book
- no laptop, no calculators
- 1 cheat-sheet permitted (1 double-sided letter-sized sheet)
- multiple choice
- short-answer Qs
- data visualization & interpretation
- statistical tests & interpretation
- generally very similar to the homeworks
Data Transformation
- rarely do we get data in exactly the format we need
- create new variables
- create summaries of variables (counts, means, sds)
- rename variables
- reorder variables
- lots more!
The dplyr package
- core package of the
tidyverse - https://dplyr.tidyverse.org/
- a grammar of data manipulation

The dplyr package
- provides a set of verbs that help you manipulate data

The nycflights13 dataset
- https://github.com/tidyverse/nycflights13
- all flights that departed from New York City area airports in 2013
- to destinations in the USA, Puerto Rico, and the American Virgin Islands
- 33,776 flights in total
- contains 5 separate data tables
flights: all flights departing NYC in 2013—today we will use thisweather: hourly meterological data for each airportplanes: construction info about each planeairports: airport names and locationsairlines: translation between two-letter airline codes and names
Install the nycflights13 package
only have to do this once
Load required packages
must do this each time you start RStudio
flights
# A tibble: 336,776 × 19
year month day dep_time sched_dep_time dep_delay arr_time sched_arr_time
<int> <int> <int> <int> <int> <dbl> <int> <int>
1 2013 1 1 517 515 2 830 819
2 2013 1 1 533 529 4 850 830
3 2013 1 1 542 540 2 923 850
4 2013 1 1 544 545 -1 1004 1022
5 2013 1 1 554 600 -6 812 837
6 2013 1 1 554 558 -4 740 728
7 2013 1 1 555 600 -5 913 854
8 2013 1 1 557 600 -3 709 723
9 2013 1 1 557 600 -3 838 846
10 2013 1 1 558 600 -2 753 745
# ℹ 336,766 more rows
# ℹ 11 more variables: arr_delay <dbl>, carrier <chr>, flight <int>,
# tailnum <chr>, origin <chr>, dest <chr>, air_time <dbl>, distance <dbl>,
# hour <dbl>, minute <dbl>, time_hour <dttm>flights
Rows: 336,776
Columns: 19
$ year <int> 2013, 2013, 2013, 2013, 2013, 2013, 2013, 2013, 2013, 2…
$ month <int> 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1…
$ day <int> 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1…
$ dep_time <int> 517, 533, 542, 544, 554, 554, 555, 557, 557, 558, 558, …
$ sched_dep_time <int> 515, 529, 540, 545, 600, 558, 600, 600, 600, 600, 600, …
$ dep_delay <dbl> 2, 4, 2, -1, -6, -4, -5, -3, -3, -2, -2, -2, -2, -2, -1…
$ arr_time <int> 830, 850, 923, 1004, 812, 740, 913, 709, 838, 753, 849,…
$ sched_arr_time <int> 819, 830, 850, 1022, 837, 728, 854, 723, 846, 745, 851,…
$ arr_delay <dbl> 11, 20, 33, -18, -25, 12, 19, -14, -8, 8, -2, -3, 7, -1…
$ carrier <chr> "UA", "UA", "AA", "B6", "DL", "UA", "B6", "EV", "B6", "…
$ flight <int> 1545, 1714, 1141, 725, 461, 1696, 507, 5708, 79, 301, 4…
$ tailnum <chr> "N14228", "N24211", "N619AA", "N804JB", "N668DN", "N394…
$ origin <chr> "EWR", "LGA", "JFK", "JFK", "LGA", "EWR", "EWR", "LGA",…
$ dest <chr> "IAH", "IAH", "MIA", "BQN", "ATL", "ORD", "FLL", "IAD",…
$ air_time <dbl> 227, 227, 160, 183, 116, 150, 158, 53, 140, 138, 149, 1…
$ distance <dbl> 1400, 1416, 1089, 1576, 762, 719, 1065, 229, 944, 733, …
$ hour <dbl> 5, 5, 5, 5, 6, 5, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 5, 6, 6, 6…
$ minute <dbl> 15, 29, 40, 45, 0, 58, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 59, 0…
$ time_hour <dttm> 2013-01-01 05:00:00, 2013-01-01 05:00:00, 2013-01-01 0…flights
<int>: integer<dbl>: double (real numbers, i.e. with decimals)<chr>: character vector (sometimes called strings)<dttm>: date-times (a date plus a time)
other variable types
<lgl>: logical (boolean values i.e.TRUEorFALSE)<fctr>: factors- R uses these to represent categorical variables with fixed values
- we will use these when we get to ANOVA
<date>: dates
dplyr basic verbs
- pick observations (rows) by their values with
filter() - reorder observations (rows) with
arrange() - pick variables (columns) by their names with
select() - create new variables (columns) from existing data with
mutate() - collapse many values down to a summary with
summarise()
1. filter()
1. Filter rows with filter()
# A tibble: 336,776 × 19
year month day dep_time sched_dep_time dep_delay arr_time sched_arr_time
<int> <int> <int> <int> <int> <dbl> <int> <int>
1 2013 1 1 517 515 2 830 819
2 2013 1 1 533 529 4 850 830
3 2013 1 1 542 540 2 923 850
4 2013 1 1 544 545 -1 1004 1022
5 2013 1 1 554 600 -6 812 837
6 2013 1 1 554 558 -4 740 728
7 2013 1 1 555 600 -5 913 854
8 2013 1 1 557 600 -3 709 723
9 2013 1 1 557 600 -3 838 846
10 2013 1 1 558 600 -2 753 745
# ℹ 336,766 more rows
# ℹ 11 more variables: arr_delay <dbl>, carrier <chr>, flight <int>,
# tailnum <chr>, origin <chr>, dest <chr>, air_time <dbl>, distance <dbl>,
# hour <dbl>, minute <dbl>, time_hour <dttm>1. Filter rows with filter()
- grab a subset of observations (rows) based on their values
# A tibble: 842 × 19
year month day dep_time sched_dep_time dep_delay arr_time sched_arr_time
<int> <int> <int> <int> <int> <dbl> <int> <int>
1 2013 1 1 517 515 2 830 819
2 2013 1 1 533 529 4 850 830
3 2013 1 1 542 540 2 923 850
4 2013 1 1 544 545 -1 1004 1022
5 2013 1 1 554 600 -6 812 837
6 2013 1 1 554 558 -4 740 728
7 2013 1 1 555 600 -5 913 854
8 2013 1 1 557 600 -3 709 723
9 2013 1 1 557 600 -3 838 846
10 2013 1 1 558 600 -2 753 745
# ℹ 832 more rows
# ℹ 11 more variables: arr_delay <dbl>, carrier <chr>, flight <int>,
# tailnum <chr>, origin <chr>, dest <chr>, air_time <dbl>, distance <dbl>,
# hour <dbl>, minute <dbl>, time_hour <dttm>1. Filter rows with filter()
R either prints out the results, or saves them to a variable. If you want to do both, you can wrap the assignment in parentheses:
will print out to screen but not save to a var
will save to var but not print to screen
will do both
1. Filter rows with filter()
1. Filter rows with filter()
# A tibble: 842 × 19
year month day dep_time sched_dep_time dep_delay arr_time sched_arr_time
<int> <int> <int> <int> <int> <dbl> <int> <int>
1 2013 1 1 517 515 2 830 819
2 2013 1 1 533 529 4 850 830
3 2013 1 1 542 540 2 923 850
4 2013 1 1 544 545 -1 1004 1022
5 2013 1 1 554 600 -6 812 837
6 2013 1 1 554 558 -4 740 728
7 2013 1 1 555 600 -5 913 854
8 2013 1 1 557 600 -3 709 723
9 2013 1 1 557 600 -3 838 846
10 2013 1 1 558 600 -2 753 745
# ℹ 832 more rows
# ℹ 11 more variables: arr_delay <dbl>, carrier <chr>, flight <int>,
# tailnum <chr>, origin <chr>, dest <chr>, air_time <dbl>, distance <dbl>,
# hour <dbl>, minute <dbl>, time_hour <dttm>Comparisons
- comparison operators let you select observations you want based on their values
>greater>=greater or equal<less<=less or equal==equal
Comparisons
- GOTCHA: using
=when you mean===is the assignment operatora=bis an instruction to assign the value of the variablebto the variablea
==is the equal-to operatora==bis an expression that asks a question, “is a equal to b?” and evalues to a booleanTRUEorFALSE
Comparisons
- GOTCHA AGAIN!
- floating-point numbers and
== - try this in RStudio:
Comparisons
- Computers represent numbers in binary (base 2) with finite precision
- some numbers in base 2 have infinitely repeating digits (like 1/3 in base 10)
- some mathematical operations involve finite precision error
- every number you see is an approximation
Comparisons
- fix: use
near()instead of==
Logical operators
&and|or!notxor(x,y)exclusive-or
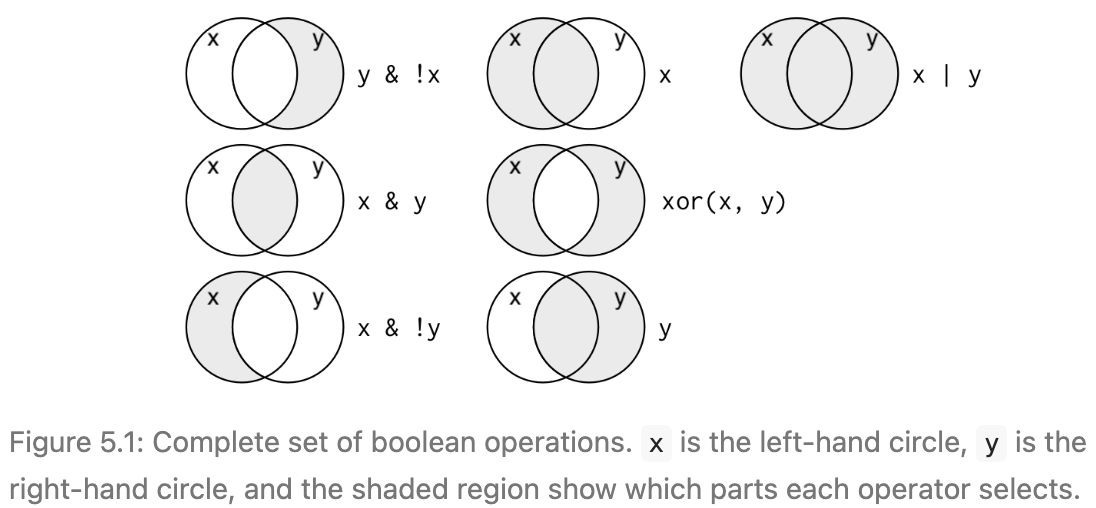
Logical operators
- Flights that departed in November or in December
- Flights that were not delayed on arrival or departure by greater than 15 minutes
Missing values
- R uses the value
NAto denote missing values
(“Not Available”) NAs are “contagious”
Missing values
- good news:
filter()only includes observations (rows) where the condition isTRUE - by default it excludes both
FALSEandNAvalues
2. arrange()
2. Arrange rows with arrange()
- like
filter()but instead of selecting rows, it changes their order - it’s like doing a “sort” in Microsoft Excel
# A tibble: 336,776 × 19
year month day dep_time sched_dep_time dep_delay arr_time sched_arr_time
<int> <int> <int> <int> <int> <dbl> <int> <int>
1 2013 1 1 517 515 2 830 819
2 2013 1 1 533 529 4 850 830
3 2013 1 1 542 540 2 923 850
4 2013 1 1 544 545 -1 1004 1022
5 2013 1 1 554 600 -6 812 837
6 2013 1 1 554 558 -4 740 728
7 2013 1 1 555 600 -5 913 854
8 2013 1 1 557 600 -3 709 723
9 2013 1 1 557 600 -3 838 846
10 2013 1 1 558 600 -2 753 745
# ℹ 336,766 more rows
# ℹ 11 more variables: arr_delay <dbl>, carrier <chr>, flight <int>,
# tailnum <chr>, origin <chr>, dest <chr>, air_time <dbl>, distance <dbl>,
# hour <dbl>, minute <dbl>, time_hour <dttm>2. Arrange rows with arrange()
- like
filter()but instead of selecting rows, it changes their order - it’s like doing a “sort” in Microsoft Excel
# A tibble: 336,776 × 19
year month day dep_time sched_dep_time dep_delay arr_time sched_arr_time
<int> <int> <int> <int> <int> <dbl> <int> <int>
1 2013 12 7 2040 2123 -43 40 2352
2 2013 2 3 2022 2055 -33 2240 2338
3 2013 11 10 1408 1440 -32 1549 1559
4 2013 1 11 1900 1930 -30 2233 2243
5 2013 1 29 1703 1730 -27 1947 1957
6 2013 8 9 729 755 -26 1002 955
7 2013 10 23 1907 1932 -25 2143 2143
8 2013 3 30 2030 2055 -25 2213 2250
9 2013 3 2 1431 1455 -24 1601 1631
10 2013 5 5 934 958 -24 1225 1309
# ℹ 336,766 more rows
# ℹ 11 more variables: arr_delay <dbl>, carrier <chr>, flight <int>,
# tailnum <chr>, origin <chr>, dest <chr>, air_time <dbl>, distance <dbl>,
# hour <dbl>, minute <dbl>, time_hour <dttm>2. Arrange rows with arrange()
- use
desc()to re-order by a column in descending order
# A tibble: 336,776 × 19
year month day dep_time sched_dep_time dep_delay arr_time sched_arr_time
<int> <int> <int> <int> <int> <dbl> <int> <int>
1 2013 1 9 641 900 1301 1242 1530
2 2013 6 15 1432 1935 1137 1607 2120
3 2013 1 10 1121 1635 1126 1239 1810
4 2013 9 20 1139 1845 1014 1457 2210
5 2013 7 22 845 1600 1005 1044 1815
6 2013 4 10 1100 1900 960 1342 2211
7 2013 3 17 2321 810 911 135 1020
8 2013 6 27 959 1900 899 1236 2226
9 2013 7 22 2257 759 898 121 1026
10 2013 12 5 756 1700 896 1058 2020
# ℹ 336,766 more rows
# ℹ 11 more variables: arr_delay <dbl>, carrier <chr>, flight <int>,
# tailnum <chr>, origin <chr>, dest <chr>, air_time <dbl>, distance <dbl>,
# hour <dbl>, minute <dbl>, time_hour <dttm>3. select()
3. Select columns with select()
grabs all observations (rows) but only selected columns
3. Select columns with select()
grabs all observations (rows) but only selected columns
3. Select columns with select()
grabs all observations (rows) but only selected columns
# A tibble: 336,776 × 16
dep_time sched_dep_time dep_delay arr_time sched_arr_time arr_delay carrier
<int> <int> <dbl> <int> <int> <dbl> <chr>
1 517 515 2 830 819 11 UA
2 533 529 4 850 830 20 UA
3 542 540 2 923 850 33 AA
4 544 545 -1 1004 1022 -18 B6
5 554 600 -6 812 837 -25 DL
6 554 558 -4 740 728 12 UA
7 555 600 -5 913 854 19 B6
8 557 600 -3 709 723 -14 EV
9 557 600 -3 838 846 -8 B6
10 558 600 -2 753 745 8 AA
# ℹ 336,766 more rows
# ℹ 9 more variables: flight <int>, tailnum <chr>, origin <chr>, dest <chr>,
# air_time <dbl>, distance <dbl>, hour <dbl>, minute <dbl>, time_hour <dttm>3. Select columns with select()
helper functions to use with select():
starts_with("abc")matches column names that begin with “abc”ends_with("xyz")contains("ijk")matches column names that contain “ijk”num_range("x", 1:3)matchesx1,x2, andx3- read the help documentation by typing
?selectfor more
4. mutate()
4. Add new variables with mutate()
- creates new columns (variables) that are functions of existing columns
- always adds variables (columns) to the end of the dataset
- remember in RStudio easiest way to see all columns is
View()
4. Add new variables with mutate()
Let’s first chop out a chunk of the full data table so we have fewer columns, to make it easier to see how mutate() works
# A tibble: 336,776 × 7
year month day dep_delay arr_delay distance air_time
<int> <int> <int> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 2013 1 1 2 11 1400 227
2 2013 1 1 4 20 1416 227
3 2013 1 1 2 33 1089 160
4 2013 1 1 -1 -18 1576 183
5 2013 1 1 -6 -25 762 116
6 2013 1 1 -4 12 719 150
7 2013 1 1 -5 19 1065 158
8 2013 1 1 -3 -14 229 53
9 2013 1 1 -3 -8 944 140
10 2013 1 1 -2 8 733 138
# ℹ 336,766 more rows4. Add new variables with mutate()
Let’s create a new column called gain that tells us how much time each flight made up between the departure delay dep_delay and the arrival delay arr_delay:
# A tibble: 336,776 × 8
year month day dep_delay arr_delay distance air_time gain
<int> <int> <int> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 2013 1 1 2 11 1400 227 -9
2 2013 1 1 4 20 1416 227 -16
3 2013 1 1 2 33 1089 160 -31
4 2013 1 1 -1 -18 1576 183 17
5 2013 1 1 -6 -25 762 116 19
6 2013 1 1 -4 12 719 150 -16
7 2013 1 1 -5 19 1065 158 -24
8 2013 1 1 -3 -14 229 53 11
9 2013 1 1 -3 -8 944 140 5
10 2013 1 1 -2 8 733 138 -10
# ℹ 336,766 more rows4. Add new variables with mutate()
and let’s also add a column that computes the average speed of the flight (distance divided by air time):
# A tibble: 336,776 × 9
year month day dep_delay arr_delay distance air_time gain speed
<int> <int> <int> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 2013 1 1 2 11 1400 227 -9 370.
2 2013 1 1 4 20 1416 227 -16 374.
3 2013 1 1 2 33 1089 160 -31 408.
4 2013 1 1 -1 -18 1576 183 17 517.
5 2013 1 1 -6 -25 762 116 19 394.
6 2013 1 1 -4 12 719 150 -16 288.
7 2013 1 1 -5 19 1065 158 -24 404.
8 2013 1 1 -3 -14 229 53 11 259.
9 2013 1 1 -3 -8 944 140 5 405.
10 2013 1 1 -2 8 733 138 -10 319.
# ℹ 336,766 more rows4. Add new variables with mutate()
If you only want the new columns and not the old ones, use transmute():
4. Add new variables with mutate()
Be sure to go through section 5.5.1 of R for Data Science “Useful creation functions” to read about the operators and functions you can use with mutate() to create new columns by combining and computing based on existing columns
5. summarise()
5. Grouped summaries with summarise()
The summarise() verb collapses a data frame down to a single row:
5. Grouped summaries with summarise()
summarise() is much more useful when we pair it with group_by():

5. Grouped summaries with summarise()
summarise() paired with group_by():
# A tibble: 365 × 3
# Groups: month [12]
month day delay
<int> <int> <dbl>
1 1 1 11.5
2 1 2 13.9
3 1 3 11.0
4 1 4 8.95
5 1 5 5.73
6 1 6 7.15
7 1 7 5.42
8 1 8 2.55
9 1 9 2.28
10 1 10 2.84
# ℹ 355 more rows5. Grouped summaries with summarise()
summarise() paired with group_by():
5. Grouped summaries with summarise()
summarise() paired with group_by(): 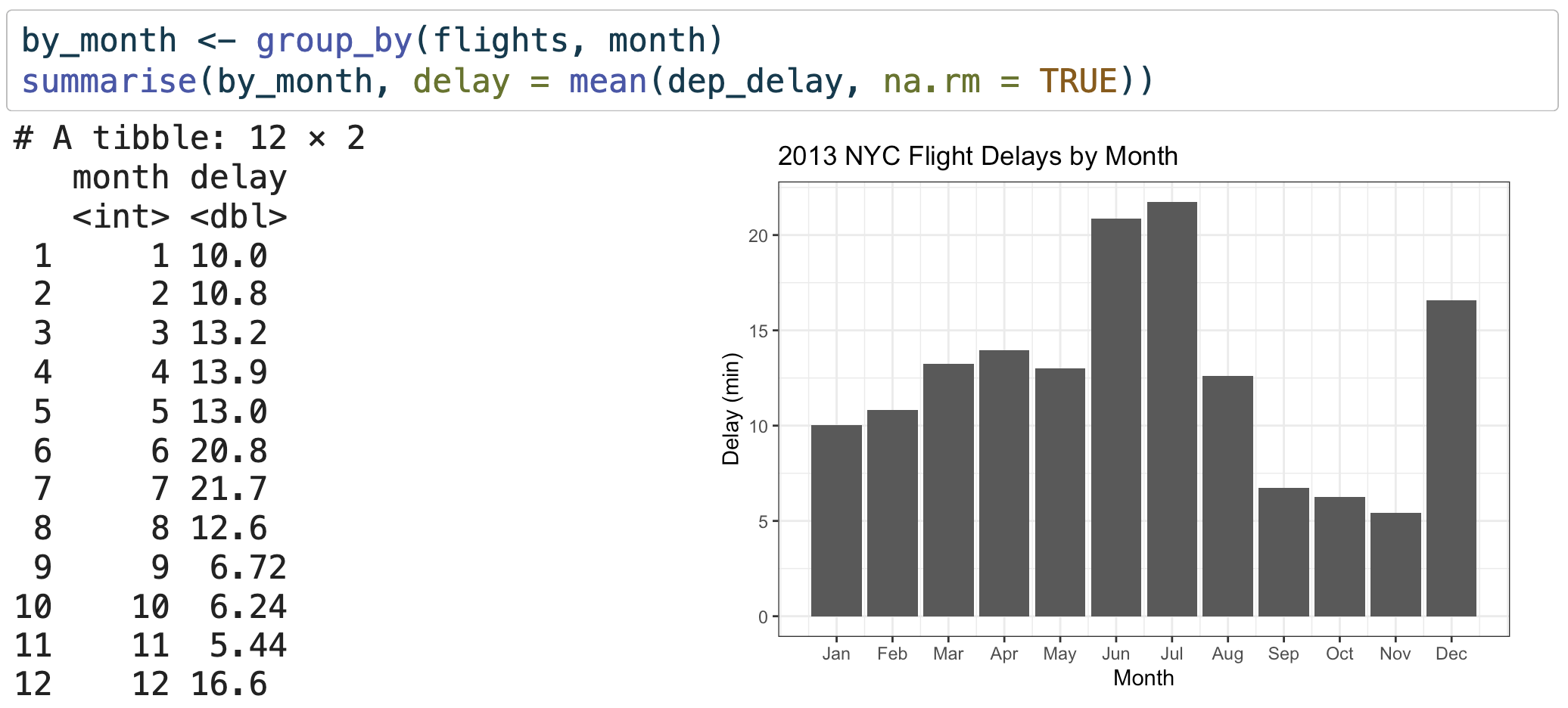
Multiple wrangles
by_dest <- group_by(flights, dest)
delay <- summarise(by_dest,
count = n(),
dist = mean(distance, na.rm = TRUE),
delay = mean(arr_delay, na.rm = TRUE)
)
delay <- filter(delay, count > 20, dest != "HNL")
# It looks like delays increase with distance up to ~750 miles
# and then decrease. Maybe as flights get longer there's more
# ability to make up delays in the air?
ggplot(data = delay, mapping = aes(x = dist, y = delay)) +
geom_point(aes(size = count), alpha = 1/3) +
geom_smooth(se = FALSE)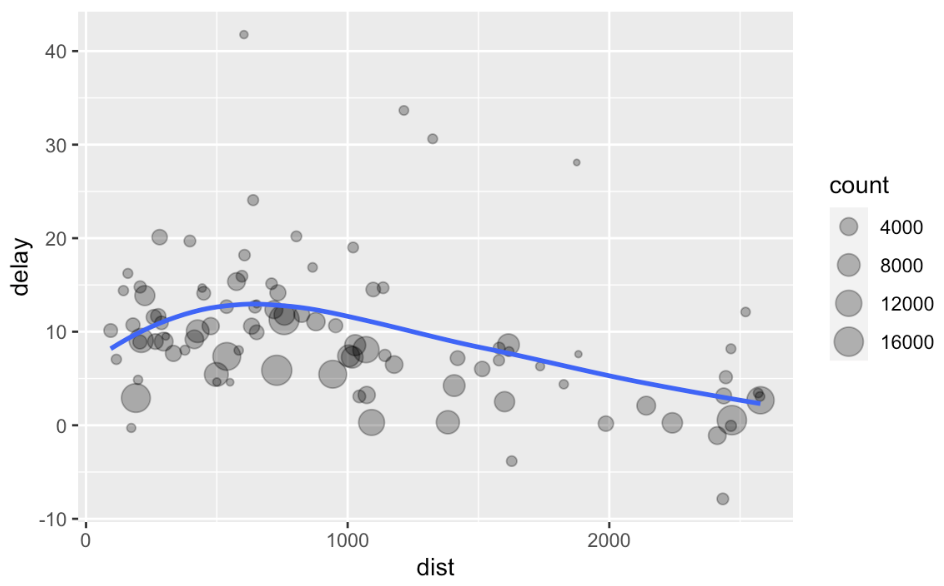
Multiple wrangles: %>%
delays <- flights %>%
group_by(dest) %>%
summarise(
count = n(),
dist = mean(distance, na.rm = TRUE),
delay = mean(arr_delay, na.rm = TRUE)
) %>%
filter(count > 20, dest != "HNL")
ggplot(data = delays, mapping = aes(x = dist, y = delay)) +
geom_point(aes(size = count), alpha = 1/3) +
geom_smooth(se = FALSE)
5. Grouped summaries with summarise()
Useful summary functions
count(),min(),max(),quantile(),mean(),median(),sd()- read R for Data Science section 5.6.4 for a longer list
Summary of today
- we learned five
dplyrverbs for wrangling data:filter()arrange()select()mutate()summarise()(paired withgroup_by())